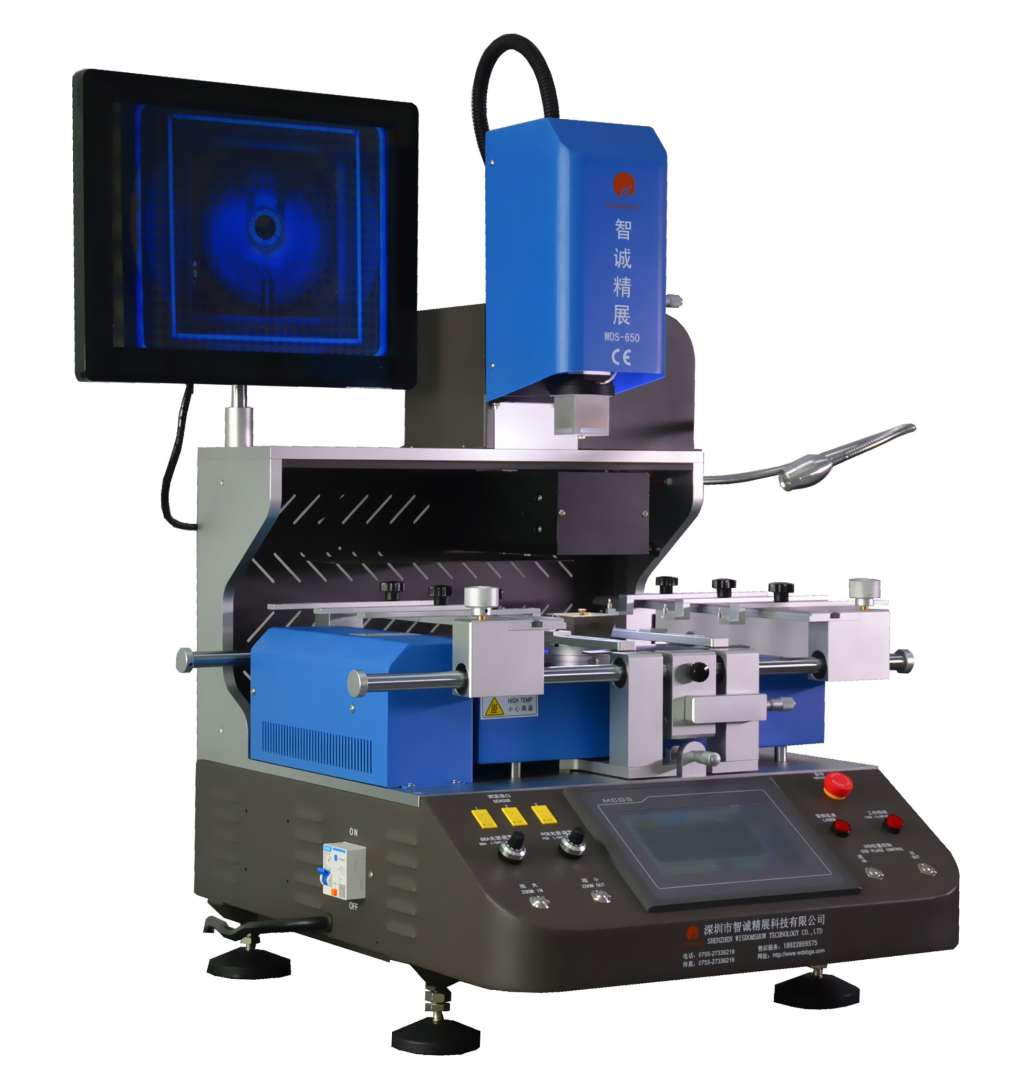
Workers utilize BGA rework stations to modify PCBs with surface-mounted and BGA-attached electronics components. Rework stations may be considered as facilities where technicians can change circuit boards and surface-mounted gadgets using BGA packaging and BGA rework stencil kit.
Technicians can conduct repairs, reworks, and refinishes on BGA rework stations. These workstations also allow operators to reinstall wrongly attached components, remove faulty components, replace missing components, and remove damaged components. Moreover, these stations are known as SMD (surface-mounted devices) or SMT (surface mounted technologies), depending on the type of device they are used for.
Typical Mistakes in BGA Rework
BGA rework relies much on science, but it also relies heavily on art. Knowledge of the rework phenomena and handling sensitive components is essential for the operator. As a result, BGA Rework is one of the industry’s most complicated and time-consuming processes. Some frequent BGA Rework blunders to watch out for:
- Operator Training That Is Not Appropriate
Rework specialists should have a wide range of experience, the right training, and the ability to use their knowledge effectively. To do BGA rework, a technician must thoroughly understand the equipment, materials utilized, and procedures. Technicians need to accurately measure the progress of BGA repairs and scale them accordingly. Detecting when things are going astray is something he must be able to do.
- Selecting the Wrong Tools
There is no substitute for the proper tools for BGA rework. The equipment must be able to meet the needs of the project. Predictability, repeatability, and control must be maintained.
Thermal management and sensing, as well as the ability to replace and remove the device, are all included in this. As a result, you must utilize the best equipment possible to ensure that your BGA repairs are of the highest quality.
- Inadequate Profile Development
A repeatable and successful BGA rework procedure is impossible without an accurate BGA to rework profile. The BGA assembly or its components might be damaged if its thermal profile is not properly established.
An increase in the number of rework cycles may be necessary as a result. To create high-quality profiles, the operator must pay close attention to the placement and analysis of thermocouples.
- Inadequate post-installation inspection
With the naked eye, it’s impossible to see what’s behind a BGA component. On the other hand, modern X-ray technologies allow us to view beneath the BGA component itself. Problems including improper positioning, excessive voiding, and misalignment can be avoided by using this method.
An operator must be trained appropriately to grasp and interpret the image created by X-ray equipment correctly. The BGA component’s intricacy and the X-ray image variances need optimal utilization of this advanced technology.
Advantages of BGA Rework Stations
- Accuracy
Complexity and mastery are required to operate the BGA rework station effectively and efficiently. When attempting to rework a BGA, you run the risk of damaging or destroying the entire PCB. It is possible to finish the rework safely and correctly without causing any harm to the device by employing these rework stations’ essential instruments.
- Efficiency
Specialized equipment including solder balls, pick-up tubes, and nozzles are commonly used in BGA rework stations to help ensure that the reworking task is completed effectively by skilled professionals
- Volume
BGA rework stations can help organizations like equipment makers do a high number of jobs on various PCBs.
- Cost
Purchasing a BGA rework station is a wise financial decision. It is possible to extend the life of your PCB through rework. Moreover, reworking a PCB is less expensive than purchasing or constructing a new one.
Types of BGA Rework Stations
- Hot-air rework stations – The BGAs are heated using hot air at these rework stations. Nozzles of variable diameter send hot air onto the damaged portion of the circuit board.
- Infrared (IR) rework stations – Several types of heat lamps and beams may be used to rework BGAs using these stations. Various IR rework stations employ ceramic heaters, and they use louvers to isolate the BGA’s specific regions of focus. Focus beams are used in the upper-tier IR rework stations to isolate the BGA while avoiding heat damage to the nearby areas.
How to select the appropriate BGA rework station?
There are advantages and disadvantages to both types of rework stations. There are several factors that go into deciding whether or not to use hot air or infrared (IR) heating for your business.
- Temperature Regulating Device
The heated air is directed upward in hot-air rework stations, and a board heater is used to heat the lower area. Bottom-side hot air isn’t available in the IR rework stations. It’s common to utilize a heat lamp with a black diffuser to heat the BGA on IR rework stations uniformly
- Efficiency
Nozzles on the hot air rework stations direct the airflow to specific parts of the BGA. IR workstations do not require nozzles since the operator may refocus each beam.