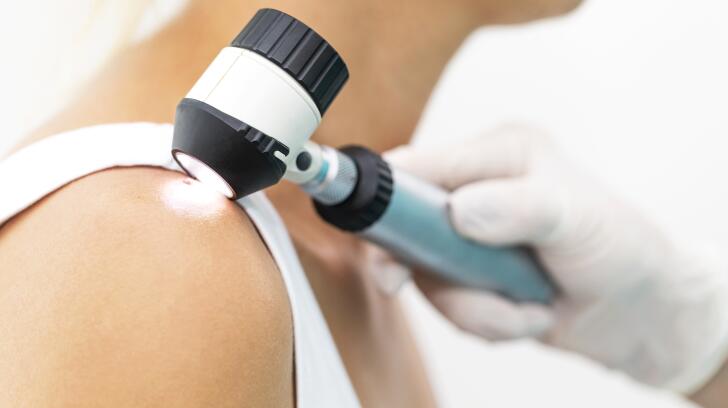
Because Australians have fair skin and light red hair and eyes, they top the world in skin cancer cases. Skin cancer primarily affects the face, back, and legs. Skin cancer is caused by UV radiation from the sun, but it can also be caused by tanning booths. It can grow in any region of the body. People with fair skin, red eyes or hair, many moles, a family history of skin cancer, sunburns, and long-term sun exposure are at risk for skin cancer. If you’re in Sydney and need assistance, go to Sundoctor Australia or a skin cancer clinic, Melbourne for a cost-effective skin cancer check. Make an appointment with a dermatologist or skin expert who uses a computer scan program and has years of experience detecting skin cancers such as melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. The following information is provided by the skin cancer clinic: –
Risky Factors Responsible for Skin Cancer:-
- Skin Colour:- If you have fair skin, light-colored eyes, and blond hair, you’re more likely to get skin cancer since your skin’s melanin/pigment can’t protect you from UV radiation.
- Sunburn:- Blistering sunburns in children or teenagers raise the risk of skin cancer in adults. Another risk factor for skin cancer in adults is sunburn.
- Extra Exposure to Sun:- Excessive sun exposure can lead to skin cancer if the skin is not protected with sunscreen or protective clothes. Other variables include tanning as a result of increased UV exposure, as well as exposure to tanning beds and lamps.
- High temperatures:- People who live at higher altitudes are more exposed to radiation than those who live in colder regions. More sun exposure can lead to skin cancer.
- Moles:- Skin cancer is more likely in people who have many atypical moles. If you have a history of atypical moles, keep an eye on them because these irregular, big moles can become malignant.
- Precancerous Moles:- The development of actinic keratosis cells, which appear as rough, scaly patches ranging from brown to dark pink, raises the risk of skin cancer. They appear on the face, head, and hands of people with pale skin who have been exposed to the sun.
- A personal or family history:- If you’ve had skin cancer before or if anyone in your family has had skin cancer, you’re at a higher risk.
- Weak immune system:- People with HIV/AIDS, as well as those who have had an organ transplant and are receiving medicines to enhance their immune systems, are more likely to develop skin cancer.
- Exposer to substances and radiation:- Skin cancer, particularly basal cell carcinoma, is more common in people who have received laser treatment for acne or eczema. Exposure to substances like arsenic increases your chances of developing skin cancer.
Conclusion:- Examine yourself in the mirror to see if you’re at risk for skin cancer. Examine your new skin growth and keep track of the changes. Examine your face, head, neck, scalp, chest, back, trunk, legs, and feet, among other areas of your body, and visit a doctor if you detect anything unusual or abnormal. Protect your skin from UV radiation to keep it safe and healthy & the best website is here. Avoid sun-sensitizing medications such as antibiotics by wearing sunglasses and wearing protective clothing. If in doubt, hire the most efficient, licensed, and experienced doctors.